Your credit score is an important number that reflects the information in your credit report. The score summarizes your credit history, which lenders use to help predict how likely it is that you will repay a loan and make payments when they are due. Lenders may use credit scores in deciding whether to grant you credit, what terms you are offered, and the interest rate you will pay on a loan.
When you apply for credit or a loan, your credit score allows you to get an answer faster. Credit scores help lenders make decisions based on financial factors, because they objectively measure the applicant’s risk profile. Credit scores also reflect recent payment patterns, so past credit problems are less likely to influence current loan requests.
How is my credit score calculated?
To calculate a credit score, your credit report must contain enough information on which to base a score. Generally, this means you must have at least one account that has been open for six months or longer, and activity in that account must have been reported to a credit bureau within the past six months.
Your credit score is based solely on the information in your credit report retained by the company calculating your score. If you obtain a credit score from another credit bureau, it may be different because of the information on file for you.
Types of credit: 10%
Payment history: 35%
Amounts owed: 30%
Length of credit history: 15%
New credit 10%
Note: Credit score calculations vary by credit bureau.
What factors are considered?
The factors impacting a credit score vary depending on the scoring model or formula being used. Your credit score is generally affected by the information contained in your credit report. For example, the number of accounts with a balance (too many accounts could indicate over-extension), the amount owed on specific types of accounts (credit cards, car loans, student loans, residential mortgages, etc.), and the total amount owed across all accounts.
Other considerations include whether you pay your bills on time, have any collection actions against you, and the age of your accounts. Credit utilization is another important variable. If you are close to maxing out your available credit lines, you might have trouble making payments in the future. The number of new accounts recently opened, and whether you have been “rate shopping” for a single loan, are additional elements affecting your credit score.
What factors are not considered?
Under federal law, everyone has an equal opportunity in applying for credit. Your race, color, religion, national origin, gender, marital status, age, or any income received from a public assistance program, cannot be used in a credit scoring formula. Other factors omitted are your salary, occupation, title, employer, or employment history. However, lenders may consider your salary and employment information in making their overall credit approval decisions. Where you live and certain types of inquiries or requests for your credit report also do not affect your credit score.
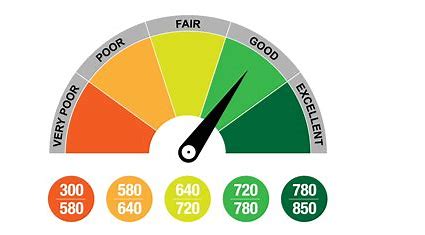
What is a good credit score?
One of the most popular brands of credit scores is the FICO Score, created by the Fair Isaac Corporation. The FICO Score is used by most lenders, and typically ranges from 300 (very poor) to 850 (exceptional). However, there are numerous FICO scoring models, and each of the three nationwide credit bureaus has its own FICO variation. The credit bureaus also have their own proprietary scoring models, often promoted as “educational scores” for consumers. Another popular brand of credit scores is VantageScore, developed as a joint venture by the three nationwide credit bureaus. The latest VantageScore model ranges from 300 (very poor) to 850 (excellent).
A good FICO Score falls between 670 and 739, while an exceptional score measures 800 and above. A good VantageScore ranges from 700 to 749, while an excellent score is 750 and above. The higher the number, the lower the perceived credit risk. Keep in mind, however, each lender has its own standards and approval process. There is no single or uniform “cutoff score” used by all lenders. Many additional factors are considered to determine actual loan terms and interest rates.
Why does my credit score matter?
Having good credit is important. It determines whether you will qualify for a loan, and, if you do, what terms you will receive. Depending on the interest rate of the loan for which you qualify, it could mean the difference between hundreds and even thousands of dollars in savings over the life of the loan. A good credit score could also determine whether you are able to rent the apartment you want, or even get mobile phone or internet services you need.
What can cause my credit score to change?
Because your credit score reflects the information in your credit report, changes to your credit report may cause your credit score to change. For instance, if you pay your bills late or incur more debt, your credit score may go down. However, if you pay down an outstanding balance on a credit card or mortgage, or correct an error in your credit report, your credit score may go up.
How can I get my credit score?
In some cases, a lender may tell you your credit score for free when you apply for credit. For example, if you apply for a mortgage, you may receive the credit score or scores that were used to determine whether the lender would extend credit to you and on what terms. You may also receive a free credit score or scores from lenders when you apply for other types of credit, such as a car loan or a credit card. If not provided, it will not hurt to ask the lender about your score.
You may also purchase your credit score from any of the nationwide credit bureaus by calling them or visiting their websites.
Equifax: Call 1-800-685-1111 or
visit www.equifax.com/compare-products
Experian: Call 1-888-397-3742 or
visit www.experian.com/consumer-products/credit-score.html
TransUnion: Call 1-800-493-2392 or
visit www.transunion.com/credit-score
How can I improve my credit score?
To find out steps you can take to improve your credit score, read the Federal Reserve Board’s 5 Tips: Improving Your Credit Score.